Tariffs, Duties, and Taxes Explained: A Complete Guide to Import Fees
Expanding your business internationally? Understanding tariffs, duties, and taxes is critical to avoiding unexpected costs and maintaining profitability. This guide breaks down these fees, explains how they’re calculated, and provides actionable strategies to reduce your import expenses.
What Are Tariffs, Duties, and Taxes?
When importing goods, businesses encounter three primary fees: tariffs, duties, and taxes. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct purposes:
1. Tariffs
- Definition:A tax imposed by governments on imported goods to protect domestic industries or regulate trade.
- Purpose:Shields local businesses from foreign competition and generates revenue.
- Example:The U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on steel imports under Section 232 to boost domestic production.
2. Duties
- Definition:A fee applied to imported goods based on their value, weight, quantity, or type.
- Purpose:Varies by product category and trade agreements.
- Example:A 5% ad valorem duty on electronics imported into the EU.
>> See more: Navigating the Suspension of Section 321: Strategies for E-commerce Brands
3. Taxes
- Definition:General levies like Value Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Services Tax (GST) applied at the point of sale.
- Purpose:Funds public services and infrastructure.
- Example:A 20% VAT on imported clothing in the UK.
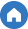
Infographic: Tariffs vs. Duties vs. Taxes
Key Differences Between Tariffs, Duties, and Taxes
| Factor | Tariffs | Duties | Taxes |
| Scope | Applied to specific goods | Varies by product type | Applied to all goods/services |
| Primary Goal | Protect local industries | Regulate trade flows | Generate government revenue |
| Calculation | Based on HS code | Product type & origin | Percentage of product value |
How Import Fees Are Calculated
1. Tariffs: The Role of HS Codes
Tariffs depend on Harmonized System (HS) codes, a 6–10 digit classification used globally. Misclassification can lead to overpayment or penalties.
- Example:Bicycles (HS 8712) face a 15% tariff in Country A but 5% in Country B under a trade agreement.
2. Duties: Product Type and Origin Matter
Duties vary by:
- Product category:Electronics vs. textiles.
- Country of origin:NAFTA (now USMCA) reduces duties for North American goods.
3. Taxes: VAT, GST, and Sales Tax
Taxes are calculated as a percentage of the product’s total value, including shipping and insurance (CIF value).
- Formula:Tax = (Product Value + Shipping + Insurance) × Tax Rate
Flowchart: How Import Fees Are Calculated
5 Common Mistakes That Inflate Import Costs
- HS Code Misclassification
- Using outdated codes or vague product descriptions.
- Fix:Use tools like the USITC Tariff Database or consult a customs broker.
- Overlooking Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Missing duty exemptions under agreements like USMCA or ASEAN.
- Ignoring Incoterms
- Not clarifying who pays fees (e.g., DDP vs. EXW shipments).
- Underestimating VAT/GST
- Forgetting to include taxes in retail pricing, hurting profit margins.
- Missing Duty Drawbacks
- Failing to reclaim duties on re-exported goods.
>> See more: Section 301 Tariffs: Impact and Adaptation Strategies for E-commerce and Beyond
4 Strategies to Reduce Import Costs
1. Leverage Free Trade Agreements
Research FTAs between your country and suppliers. For example:
- USMCA:Eliminates tariffs on 99% of goods traded between the U.S., Mexico, and Canada.
- CPTPP:Reduces duties for member countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
2. Optimize Supply Chains
- Nearshoring:Source from countries with lower tariffs.
- Bonded Warehouses:Store goods duty-free until they’re sold.
3. Work with a Customs Broker
Experts ensure accurate HS codes, paperwork, and compliance.
4. Use Duty Drawback Programs
Recover duties on imported goods later re-exported.
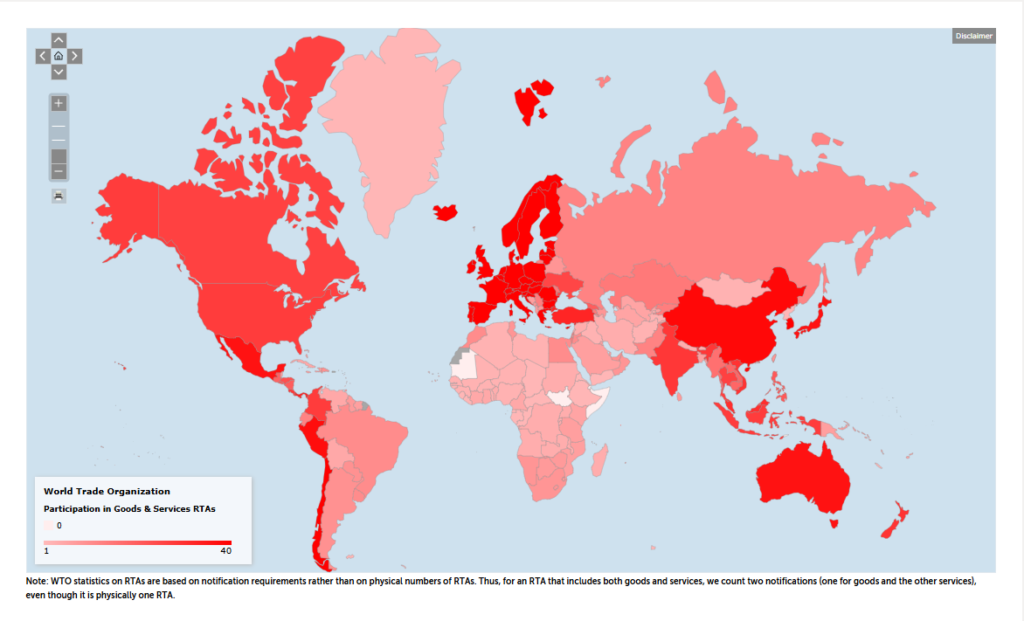
World Map Highlighting Key Trade Agreements
How Recent Trade Policies Impact Import Fees
- S.-China Trade War:Tariffs up to 25% on $350B worth of Chinese goods.
- Brexit:New VAT rules and customs checks for EU-UK trade.
- CBAM (EU):Upcoming carbon taxes on imports like steel and cement.
FAQs: Tariffs, Duties, and Taxes
Q: How do I find my product’s HS code?
A: Use the WTO HS Code Finder or consult a broker.
Q: Can I avoid VAT?
A: Businesses in some regions can reclaim VAT. For example, the EU allows VAT refunds for non-resident companies.
Q: Do duties apply to samples?
A: Often exempt if marked “No Commercial Value,” but rules vary.
Need Help Navigating Import Fees?
At Golsolution, we simplify global trade. Our experts handle HS code classification, FTA optimization, and compliance, saving you time and money.
Contact us today to streamline your imports:
📞 +65 8342 6900 | 🌐 https://golsolution.com