What is FDA QSR? Differences between FDA QSR and ISO 13485
In the realm of medical device manufacturing, compliance with regulatory standards is paramount. Two key frameworks governing quality management are the Food and Drug Administration Quality System Regulation (FDA QSR) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 13485. While both aim to ensure product safety and quality, they differ in scope, certification processes, and global applicability. In this article, join GOL in exploring the fundamentals of FDA QSR, outline its differences from ISO 13485, and highlight what they mean for manufacturers in the medical device industry.
What is FDA QSR?
The Food and Drug Administration Quality System Regulation (FDA QSR), also known as 21 CFR Part 820, outlines the requirements for medical device manufacturers to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their products. Enacted in 1978, this regulation sets forth a comprehensive framework for the design, production, distribution, and servicing of medical devices sold in the United States.
FDA QSR establishes quality management system (QMS) standards that manufacturers must adhere to throughout the product life cycle. These standards cover various aspects of device manufacturing, including design controls, production processes, quality assurance, and post-market surveillance.

One of the primary objectives of FDA QSR is to ensure that medical devices consistently meet specified quality and performance standards. By implementing QMS procedures in accordance with FDA regulations, manufacturers can minimize the risks associated with device defects, manufacturing errors, and inadequate design.
Compliance with FDA QSR is mandatory for all medical device companies selling products in the U.S. market, regardless of their size or location. Failure to meet these regulatory requirements can result in severe consequences, including product recalls, warning letters, fines, and legal penalties.
Overall, FDA QSR plays a critical role in safeguarding public health by ensuring that medical devices marketed in the United States meet rigorous quality and safety standards. By adhering to these regulations, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to producing reliable, effective, and safe products for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Read more: FSSC 22000 – Food Safety System Certification Scheme
Key Requirements of FDA QSR
Below are the key requirements of FDA QSR:
Quality Management System (QMS)
FDA QSR mandates that manufacturers establish and maintain a robust quality management system (QMS) to oversee all aspects of device design, production, distribution, and servicing. The QMS must be documented in written procedures and must cover key areas such as management responsibility, personnel training, document control, and recordkeeping.
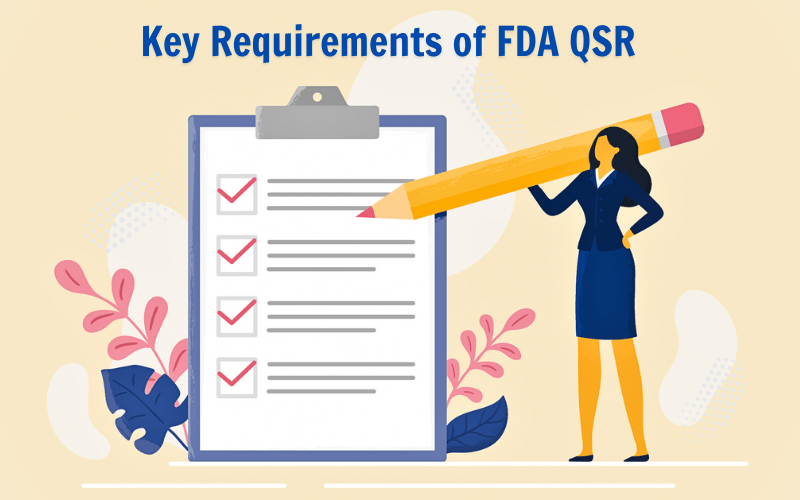
Design Controls
Manufacturers are required to implement design control procedures to ensure that medical devices meet specified design requirements and intended uses. This includes conducting risk assessments, defining design inputs and outputs, verifying design outputs, and validating design changes. Design control activities must be documented and traceable throughout the product life cycle.
Document Control
FDA QSR mandates stringent document control procedures to manage all documents related to the design, manufacturing, and distribution of medical devices. Companies must establish document control systems to ensure the accuracy, integrity, and accessibility of documents, including design specifications, procedures, work instructions, and records.
Purchasing Controls
Manufacturers must establish and maintain procedures to ensure that purchased components, materials, and services used in the production of medical devices meet specified quality and regulatory requirements. This includes evaluating and selecting suppliers, establishing purchasing specifications, and monitoring supplier performance through audits and inspections.
Production and Process Controls
FDA QSR requires manufacturers to implement controls to ensure that medical devices are consistently produced and assembled in accordance with established specifications and quality standards. This includes maintaining controlled production environments, validating manufacturing processes, and verifying the performance of production equipment.
Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Companies must establish procedures for identifying, investigating, and addressing nonconformities and quality issues related to medical devices. CAPA activities aim to prevent recurrence of problems, mitigate risks, and improve overall product quality and safety. Manufacturers are required to document and track all CAPA activities to ensure timely and effective resolution of issues.
Complaint Handling and Medical Device Reporting (MDR)
FDA QSR mandates that manufacturers have systems in place for receiving, documenting, and investigating complaints related to medical devices. Additionally, companies are required to report adverse events, device malfunctions, and serious injuries or deaths associated with their products to the FDA in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Quality System Audits
Regular audits of the QMS are essential to ensure compliance with FDA QSR requirements and identify opportunities for continuous improvement. Manufacturers must conduct internal audits of their quality system and may also undergo audits by regulatory authorities, notified bodies, or customers to assess compliance with regulatory requirements.
Management Responsibility
Top management plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and integrity of the QMS. FDA QSR requires management to establish quality policy, assign responsibilities, allocate resources, and provide leadership and support for quality initiatives. Management review meetings are conducted periodically to assess the performance of the QMS and identify areas for improvement.
In conclusion, compliance with the key requirements of FDA QSR is essential for medical device manufacturers to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of their products. By implementing robust quality management systems and adhering to regulatory requirements, companies can enhance patient safety, minimize risks, and maintain regulatory compliance in the highly regulated medical device industry.
Benefits of Complying with FDA QSR
Compliance with the Food and Drug Administration Quality System Regulation (FDA QSR) offers numerous benefits for medical device manufacturers, ranging from enhanced product quality and safety to improved market competitiveness and regulatory compliance. By adhering to FDA QSR requirements, companies can mitigate risks, streamline operations, and foster trust among stakeholders. Below are the key benefits of complying with FDA QSR:
Ensuring Product Quality and Safety
Compliance with FDA QSR standards helps ensure that medical devices meet stringent quality and safety requirements throughout the product life cycle. By implementing robust quality management systems and adhering to regulatory standards, manufacturers can minimize the risk of device defects, malfunctions, and adverse events, thereby enhancing patient safety and reducing liability risks.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
FDA QSR compliance is mandatory for medical device manufacturers selling products in the United States market. By adhering to FDA regulations and maintaining a comprehensive quality management system, companies can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties, including product recalls, warning letters, fines, and legal sanctions.
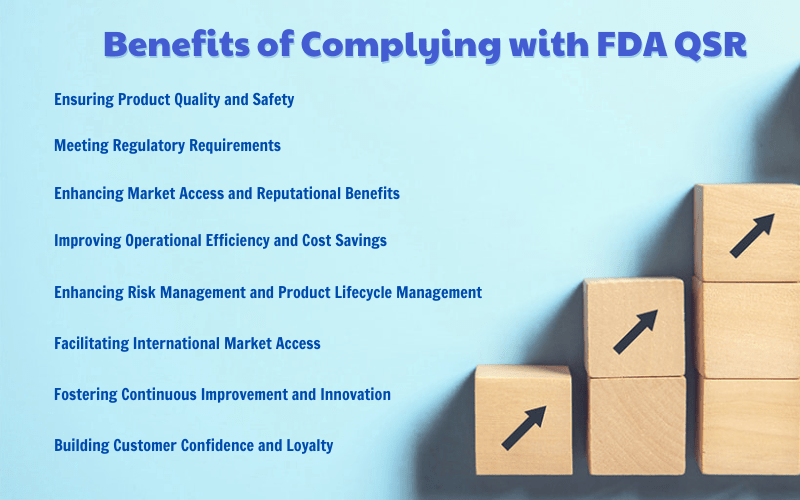
Enhancing Market Access and Reputational Benefits
Compliance with FDA QSR standards enhances a company’s credibility and reputation within the medical device industry. Manufacturers that consistently meet or exceed regulatory requirements are more likely to gain market acceptance, attract investors, and build trust among healthcare professionals, patients, and regulatory authorities. This, in turn, can facilitate market access and accelerate product adoption.
3.4. Improving Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
FDA QSR compliance encourages manufacturers to implement efficient and standardized processes throughout their organizations. By streamlining operations, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation, companies can improve productivity, minimize production errors, and achieve cost savings in the long term. Additionally, adherence to quality management principles can lead to fewer product recalls, warranty claims, and customer complaints, resulting in lower operational costs and higher profitability.
3.5. Enhancing Risk Management and Product Lifecycle Management
Compliance with FDA QSR requirements necessitates the implementation of robust risk management processes throughout the product life cycle. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with product design, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance, companies can proactively address potential issues and improve product reliability and performance. Effective risk management also enables manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding product development, regulatory submissions, and post-market surveillance activities.
3.6. Facilitating International Market Access
FDA QSR compliance can serve as a valuable foundation for companies seeking to expand their presence in international markets. Many countries and regions recognize FDA regulations as benchmarks for quality and safety assurance in medical devices. By demonstrating compliance with FDA QSR standards, manufacturers can expedite regulatory approvals, certifications, and market access in other jurisdictions, thereby enhancing global competitiveness and market reach.
3.7. Fostering Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Compliance with FDA QSR encourages a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within organizations. By regularly reviewing and updating quality management systems, companies can identify areas for optimization, implement best practices, and drive innovation in product development and manufacturing processes. Continuous improvement efforts not only enhance product quality and customer satisfaction but also ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulatory requirements and industry standards.
3.8. Building Customer Confidence and Loyalty
FDA QSR compliance demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to quality, safety, and regulatory compliance, instilling confidence in customers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory authorities. Companies that prioritize quality and adhere to regulatory standards are more likely to earn customer trust, loyalty, and repeat business. By consistently delivering safe and effective products that meet or exceed regulatory requirements, manufacturers can build long-term relationships with customers and strengthen their market position.
In summary, complying with FDA QSR offers a wide range of benefits for medical device manufacturers, including enhanced product quality and safety, regulatory compliance, market access, operational efficiency, risk management, international competitiveness, innovation, and customer satisfaction. By prioritizing quality management and regulatory compliance, companies can differentiate themselves in the marketplace, mitigate risks, and achieve sustainable business growth in the dynamic and highly regulated medical device industry.
4. Guidelines for Implementing FDA QSR
Implementing the Food and Drug Administration Quality System Regulation is crucial for medical device manufacturers to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and maintain product quality and safety. To assist companies in effectively implementing FDA QSR requirements, the following comprehensive guidelines are provided:
Understand FDA QSR Requirements
Before embarking on the implementation process, it is essential for manufacturers to thoroughly understand the requirements outlined in FDA QSR (21 CFR Part 820). This includes familiarizing themselves with the regulatory provisions, definitions, and interpretations provided by the FDA. Accessing official FDA guidance documents, training materials, and relevant publications can help clarify expectations and facilitate compliance.
Establish a Cross-Functional Implementation Team
Successful implementation of FDA QSR requires collaboration and coordination across various functional areas within the organization. Establishing a cross-functional implementation team comprising representatives from quality assurance, regulatory affairs, research and development, manufacturing, engineering, and other relevant departments is essential. This team should be tasked with overseeing the implementation process, identifying resource requirements, and ensuring alignment with organizational goals and objectives.
Conduct a Gap Analysis
Before initiating implementation activities, conduct a comprehensive gap analysis to assess the organization’s current practices and capabilities relative to FDA QSR requirements. Identify areas of non-compliance, process gaps, and resource constraints that need to be addressed to achieve compliance. The gap analysis should cover all relevant aspects of the quality management system, including design controls, production processes, document control, supplier management, and corrective actions.
Develop a Comprehensive Implementation Plan
Based on the findings of the gap analysis, develop a detailed implementation plan outlining the steps, timelines, responsibilities, and resources required to achieve compliance with FDA QSR. Break down the implementation plan into manageable tasks and milestones, prioritizing activities based on their criticality and impact on product quality and regulatory compliance. Ensure that the implementation plan is realistic, achievable, and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Establish Documented Procedures and Work Instructions
Documented procedures and work instructions are essential for ensuring consistency, repeatability, and traceability in the implementation of FDA QSR requirements. Develop written procedures covering all aspects of the quality management system, including design controls, document control, production processes, supplier management, complaint handling, and corrective actions. Clearly define roles, responsibilities, and workflow processes to guide employees in performing their tasks effectively.
Provide Training and Education
Comprehensive training and education programs are critical for ensuring that employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and the requirements of FDA QSR. Provide targeted training sessions for personnel involved in implementing and maintaining the quality management system, including quality assurance staff, production operators, engineers, and managers. Training should cover topics such as FDA regulations, quality management principles, process requirements, and documentation practices.
Implement Risk Management Practices
Risk management is an integral part of FDA QSR and involves identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks throughout the product life cycle. Implement robust risk management practices to systematically evaluate and address potential hazards, failure modes, and adverse events associated with medical devices. Utilize risk management tools and techniques such as failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), hazard analysis, and risk control strategies to minimize risks and optimize product safety and effectiveness.
Establish Controls for Design and Development
Implement robust design control procedures to ensure that medical devices meet specified design requirements, intended uses, and user needs. Establish documented processes for managing design inputs, design outputs, design verification, design validation, and design changes. Ensure that design control activities are conducted systematically, with adequate documentation and traceability to support regulatory compliance and product quality.
Implement Controls for Production and Process
Implement controls to ensure that medical devices are consistently produced and assembled in accordance with established specifications and quality standards. Develop documented procedures for controlling production processes, equipment calibration, personnel training, and environmental conditions. Conduct regular process validations, equipment qualifications, and in-process inspections to verify the performance and conformance of production processes.
Establish Procedures for Monitoring and Measurement
Develop procedures for monitoring, measurement, and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to product quality, process effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Implement systems for collecting, analyzing, and reporting data on product nonconformities, customer complaints, corrective actions, and preventive actions. Use statistical process control (SPC) techniques and trend analysis to identify patterns, detect deviations, and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Implement Controls for Supplier Management
Establish procedures for evaluating, selecting, and monitoring suppliers of components, materials, and services used in the production of medical devices. Conduct supplier audits, assessments, and performance reviews to ensure that suppliers meet specified quality and regulatory requirements. Maintain records of supplier qualifications, agreements, and communications to demonstrate compliance with FDA QSR requirements.
Implement Controls for Complaint Handling and Adverse Event Reporting
Develop procedures for receiving, documenting, investigating, and resolving complaints related to medical devices. Ensure that complaints are promptly evaluated, categorized, and escalated as necessary to address potential safety issues or regulatory concerns. Implement systems for reporting adverse events, device malfunctions, and other quality-related incidents to the FDA in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Establish Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) Processes
Develop robust CAPA processes to identify, investigate, and address nonconformities, deviations, and quality issues related to medical devices. Establish procedures for initiating, documenting, tracking, and closing CAPA actions in a timely and effective manner. Implement root cause analysis (RCA) techniques, such as fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, and fault tree analysis, to identify underlying causes and implement corrective and preventive actions to prevent recurrence.
Conduct Internal Audits and Management Reviews
Regularly conduct internal audits of the quality management system to assess compliance with FDA QSR requirements and identify areas for improvement. Establish audit schedules, checklists, and procedures for conducting comprehensive audits of all relevant processes and procedures. Additionally, conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the performance of the quality management system, review audit findings, and make data-driven decisions to drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Maintain Documentation and Records
Maintain accurate, complete, and up-to-date documentation and records to demonstrate compliance with FDA QSR requirements. Establish document control procedures for managing documents, records, revisions, and approvals throughout the document lifecycle. Ensure that all documents and records are easily accessible, retrievable, and securely stored in compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies.
Continuously Monitor, Measure, and Improve
Implement a culture of continuous improvement and regulatory compliance by monitoring, measuring, and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to product quality, process effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Utilize feedback mechanisms, customer surveys, and internal audits to identify opportunities for improvement and drive corrective and preventive actions. Regularly review and update procedures, processes, and training programs to ensure ongoing compliance with FDA QSR requirements and industry best practices.
Stay Informed and Adapt to Regulatory Changes
Keep abreast of changes, updates, and interpretations of FDA regulations and guidance documents related to medical device quality and compliance. Stay informed about emerging trends, best practices, and industry standards through participation in professional organizations, conferences, and training programs. Proactively adapt and update internal processes and procedures to incorporate regulatory changes and maintain alignment with evolving FDA requirements and expectations.
By following these guidelines, medical device manufacturers can establish robust quality management systems, achieve regulatory compliance, and ensure product quality and safety in accordance with FDA QSR requirements.
5. Differences between FDA QSR and ISO 13485?
| Items | FDA Standard |
ISO 13485 |
| Scope of Application | Applies to medical products sold or imported into the United States. | ISO 13485 is an international standard applicable to any medical device manufacturer worldwide, not limited to the United States. |
| Certification Process | Requires manufacturers to submit applications and FDA inspection records to obtain certification. The FDA conducts comprehensive evaluations of records, manufacturing processes, and batch testing before granting approval for products. | The certification process is based on the review and assessment of the manufacturer’s quality management system. Independent certification bodies authorized by ISO organize assessments and certify compliance with ISO 13485 manually. |
| Subject Control | Primarily focuses on controlling medical products and manufacturing processes of manufacturers. | Control extends not only to medical products but also to the procedures and quality management systems of manufacturing organizations. |
| Time and Frequency of Inspection | FDA inspections and checks typically occur before products are allowed to enter the market. However, the FDA also conducts random or requested inspections when necessary. | ISO 13485-certified organizations conduct regular inspections and evaluations of the manufacturer’s quality management system to ensure manual compliance. The timing and frequency of inspections are determined by the certification bodies. |
| Next Access Rights | The FDA has the authority to inspect and supervise medical manufacturers nationwide. This agency has the power to request immediate access to records, conduct on-site inspections at manufacturers, and revoke certifications if manual compliance is not met. | ISO 13485-certified organizations have the right to inspect and assess the quality management system of manufacturers. However, the authority of ISO 13485 is not comparable to the FDA’s authority in terms of enforcement and law enforcement. |
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1. How does FDA QSR impact market access and competitiveness?
Compliance with FDA QSR enhances a company’s credibility and reputation within the medical device industry, facilitating market access, attracting investors, and building trust among stakeholders. It also ensures alignment with regulatory requirements, enhancing competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
6.2. What are the key differences in the implementation guidelines between FDA QSR and ISO 13485?
While both FDA QSR and ISO 13485 provide guidelines for quality management in medical device manufacturing, differences exist in their scope, certification process, subject control, inspection, and access rights. Understanding these differences is crucial for effectively implementing the respective standards.
6.3. How does FDA QSR ensure product quality and safety?
FDA QSR establishes requirements for robust quality management systems, including design controls, production processes, document control, supplier management, and corrective actions. Compliance with these requirements helps ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy throughout the product lifecycle.
6.4. What are the documentation requirements for FDA QSR compliance?
FDA QSR mandates the maintenance of accurate and up-to-date documentation and records to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes documenting procedures, work instructions, design controls, production processes, supplier management, complaint handling, and corrective actions.
6.5. What is the role of risk management in FDA QSR compliance?
Risk management is an integral part of FDA QSR compliance, involving the identification, assessment, mitigation, and monitoring of risks associated with medical devices. Implementing robust risk management practices helps minimize potential hazards, optimize product safety, and ensure regulatory compliance.
6.6. Is compliance with both FDA QSR and ISO 13485 necessary?
While compliance with both standards is not mandatory, many medical device manufacturers choose to comply with both FDA QSR and ISO 13485 to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and international best practices. Compliance with ISO 13485 can facilitate access to international markets, while compliance with FDA QSR is essential for selling products in the United States.
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between FDA QSR and ISO 13485 is crucial for manufacturers in the healthcare and medical device industries seeking to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Each standard serves its own purpose but ultimately aims to guarantee the quality and safety of medical devices.
If you’re navigating the complexities of FDA compliance and registration, GOL Solution is here to assist. Serving over 5000+ companies with trade compliance and supply chain management solutions, GOL offers a robust array of services tailored to meet your needs, including FDA Registration, FDA Food Registration, FDA Medical Device Registration, and FDA Cosmetic Registration. Whether you are looking to understand more about QSR, ISO 13485, or need assistance with FDA registration processes, GOL is equipped to provide the guidance and support necessary to ensure compliance.
For personalized support and to learn more about how GOL can help streamline your compliance processes, contact us today at clients@golsolution.com or call our hotline at +65 8342 6900. Let GOL be your trusted partner in navigating the regulatory landscape and enhancing your company’s compliance strategy.