ISO 22000 Standard and Essential Information You Need to Know
Food safety is a top priority for consumers and businesses in the food industry. To ensure food safety and meet the increasingly high demands of the market, many enterprises have chosen to implement the ISO 22000 standard.
ISO 22000 is a food safety management system issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This standard provides a comprehensive framework for managing risks and ensuring food safety throughout the entire supply chain. In the following article, GOL will provide you with essential information about ISO 22000, so stay tuned.
What is the ISO 22000 standard?
ISO 22000 is a food safety management system standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It outlines the requirements for an organization to demonstrate its ability to control food safety hazards, ensuring that food is safe for consumption. This standard covers various aspects of food safety management, including interactive communication, system management, prerequisite programs, and the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP). It’s designed to be applicable to all organizations involved in the food chain, from farms to processing, packaging, storage, transportation, and distribution. Compliance with ISO 22000 helps companies enhance food safety, minimize risks, and build consumer confidence in their products.

Components of the ISO 22000 standard
The ISO 22000 standard for food safety management systems is a comprehensive framework that combines various elements to ensure food safety along the entire food chain, from farm to fork. Here are the key components of the ISO 22000 standard:
- Management Responsibility: Senior management must demonstrate their commitment to the FSMS by ensuring resources are available, communicating to the organization the importance of meeting food safety requirements, and establishing clear management policies.
- Food Safety Policy: This policy should be set by top management and communicate the organization’s overall objectives and direction concerning food safety.
- Food Safety Management System Planning: The organization must plan and develop the processes needed to meet the requirements of the standard, and to implement the food safety policies and objectives.
- Prerequisite Programs (PRPs): These are conditions and activities that are necessary to maintain a hygienic environment throughout the food chain suitable for the production, handling, and provision of end products.
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) principles: Based on Codex Alimentarius, this includes the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement, handling, to manufacturing, distribution, and consumption of the finished product.
- Interactive Communication: Effective communication across the food chain is essential for ensuring that all relevant food safety hazards are identified and adequately controlled at each step within the food chain.
- System Management: This integrates the overall food safety aspects into the organization’s management activities.
- Objective Setting and Planning to Achieve Them: The organization should set measurable objectives that drive the efforts to comply with the standard, and work towards continuous improvement of the FSMS.
- Resource Management: This involves the provision of adequate resources, suitable work environment, and training to the employees to effectively implement and maintain the FSMS.
- Validation, Verification, and Improvement of the FSMS: The organization must continually review and update their systems and processes to improve the effectiveness and adequacy of the FSMS, including regular updates following audits and reviews.
These components form a structured approach to food safety, emphasizing the importance of management commitment, systematic management, prerequisite programs, HACCP principles, and continuous improvement. The standard is designed to be flexible and can be tailored to any organization in the direct or indirect food chain, from feed producers, primary producers through food manufacturers, transport and storage operators, and subcontractors to retail and foodservice outlets.
Latest version of the ISO 22000 standard – ISO 22000:2018
The latest version of the ISO 22000 standard for food safety management systems is ISO 22000:2018, which was published in June 2018. This version updates the previous edition, ISO 22000:2005, reflecting new findings and further aligning it with other ISO management system standards through the common framework of a High-Level Structure (HLS). This alignment makes it easier to integrate with other management systems, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management.

Risk-based approach
It’s not difficult to envision this standard through our daily activities – wanting to cook a delicious and hygienic meal involves selecting ingredients with clear origins, freshness, clean cooking utensils, following the correct procedures, cooking thoroughly, and proper storage.
The ISO 22000:2018 standard, through its risk-based approach, aids businesses in preventing food safety risks.
Risks are required to be considered at strategic, policy, and organizational business environment levels. These may include:
- Risks stemming from external factors such as changes in legal environment, geographical location, customer needs, and partner expectations.
- Risks in capturing and implementing business opportunities during enterprise management operations.
All these risks need to be identified and assessed for their impact and influence on the safety of the certified product/service provided by the organization.
Moreover, identifying and controlling risks at the organizational level through a risk-based approach involving hazard analysis and determining critical control points (HACCP) principles throughout the organization’s processes remains maintained.
The ISO 22000:2018 standard provides requirements and guidelines for organizations involved in the food chain, from food production, farming, processing, packaging, storage, transportation, to meal provision. This standard applies to all types and sizes of food businesses. Consequently, it assists organizations in establishing an effective preventive system to prevent food safety risks.
The ISO 22000:2018 Food Safety Management System is designed based on the principles of HACCP and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) throughout the food chain. Identifying critical processes, analyzing hazards, determining critical control points, and establishing appropriate control measures combined with implementation and compliance monitoring are considered key factors leading to success
What is the ISO 22000 Food Safety Management System (FSMS)?
The Food Safety Management System (FSMS) ISO 22000:2018 refers to a framework comprising processes, procedures, and standards necessary to ensure food safety, adhering to ISO 22000 standards.
The decision to implement a food safety management system is considered a crucial strategic step for organizations to enhance their operational efficiency in the field of food safety. The key benefits that this system brings include:
- Ability to consistently provide safe food and related products and services, meeting customer requirements and legal regulations.
- Effectively addressing risks related to organizational objectives.
- Ability to operate continuously with tightly managed processes, providing necessary resources, and implementing measures to prevent or minimize negative impacts.

Read more: What is ISO 13485? Detailed explanation of the standard
Who should comply with ISO 22000?
The scope of application of ISO 22000:2018 – Food Safety Management System
ISO 22000 standard can be applied to any enterprise/organization involved in the food supply chain, whether directly or indirectly. This includes:
- Farms, fisheries, or dairy farms.
- Units specializing in processing foods such as meat, fish, and animal feed.
- Manufacturers of cereals, bread, beverages, canned foods, or frozen foods.
- Food service providers, typical examples being restaurants, fast food outlets, hotels, hospitals, and mobile food vendors.
- Storage and distribution service providers, food transportation companies.
- Facilities providing food processing equipment, additives, raw materials in food processing.
Facilities providing cleaning, sanitation, and food packaging services.
In other words, all requirements stipulated in ISO 22000:2018 can be applied to any product or service that comes into contact with food or is part of the food supply chain.
What are the principles of the ISO 22000 Food Safety Management System?
In general, the requirements of ISO 22000 are:
- Establish an overarching Food Safety Policy for your organization, developed by top management.
- Set objectives to drive your company’s efforts to comply with this policy.
- Plan and design a management system and document the system.
- Maintain records of the system’s performance.
- Establish a team with qualified individuals to form the Food Safety Team.
- Identify communication procedures to ensure effective communication with relevant external stakeholders (regulatory agencies, customers, suppliers, etc.) and internal communication.
- Have a plan for emergency situations.
- Organize leadership review meetings to assess the performance of the FSMS.
- Provide adequate resources to operate the FSMS effectively, including trained and competent staff, sufficient infrastructure, and a suitable working environment to ensure food safety.
- Adhere to HACCP principles.
- Establish a traceability system to identify products’ origins.
- Establish a system for corrective action and control of non-conforming products.
- Maintain a documented procedure for product recall.
- Control monitoring and measuring devices.
- Establish and maintain an internal audit program.
- Continuously update and improve the FSMS.

Benefits of obtaining ISO 22000 certification for businesses
Legal compliance:
- ISO 22000 certification can replace the Food Safety Certificate.
- ISO 22000 can substitute for many other food safety management standards such as GMP, HACCP, EUROGAP, BRC, SQF, IFS…
Ensuring quality sources:
- Ensures food safety quality for products, minimizing the risk of food poisoning.
- Minimizes costs associated with recalling or discarding defective, spoiled, or low-quality products.
Customer satisfaction:
- Provides products that consistently meet customer requirements and offer reliable service in the market.
- Enhances the credibility and brand of the business.
Internationally recognized as a reputable supplier:
- ISO 22000 certification is an international standard recognized worldwide.
- Businesses adopting quality management systems will be accepted throughout the supply chain.
- Increases opportunities to reach more international markets.
Business opportunities:
- Obtaining ISO 22000 certification opens up opportunities for business integration and significant growth due to increased business efficiency.
- Standardizes all activities from management to production or business operations of the enterprise.
Steps to obtain the latest ISO 22000:2018 certification
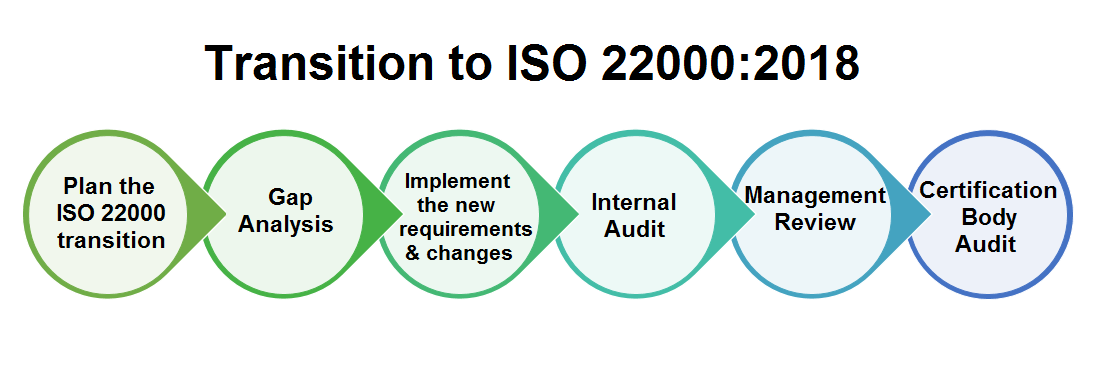
Acquiring ISO 22000:2018 certification involves implementing a food safety management system (FSMS) and undergoing an audit by an accredited certification body. Here’s a breakdown of the steps:
- Familiarization: Begin by thoroughly understanding the ISO 22000:2018 standard and its requirements. You can purchase a copy of the standard or find resources online to get familiar with the key concepts.
- Team Training: Educate your team on the principles of ISO 22000 and food safety best practices. This ensures everyone understands their role in maintaining food safety.
- Gap Analysis: Evaluate your current food safety practices against the ISO 22000 standard. This will help identify areas that need improvement to comply with the standard.
- Develop FSMS: Design your Food Safety Management System. This involves outlining policies, procedures, and documentation for all aspects of your food handling operations. The FSMS should address hazard identification, preventive controls, traceability, and continual improvement.
- Implementation: Put your FSMS into action. This involves training staff, implementing new procedures, and documenting everything.
- Internal Audits: Conduct internal audits to assess the effectiveness of your FSMS and identify any areas for improvement.
- Select Certification Body: Choose an accredited certification body to conduct the formal audit for ISO 22000:2018 compliance.
- Certification Audit: The certification body will perform an audit to verify that your FSMS meets the ISO 22000:2018 requirements. This typically involves a two-stage audit process.
- Certification: If you pass the audit, you will be awarded ISO 22000:2018 certification.
- Maintain Compliance: Maintaining certification requires ongoing commitment. You’ll need to conduct regular internal audits, review your FSMS, and make necessary improvements to ensure continued compliance.
Remember, this is a general guideline. For specific details and assistance, it’s recommended to consult with a qualified ISO 22000 consultant or your chosen certification body.
With the benefits outlined by GOL, ISO 22000 is an effective tool to help businesses improve product quality, build a reputable brand, and expand their market. Enterprises should consider implementing ISO 22000 to enhance competitive capabilities and achieve sustainable development.
Read more: