FDA regulations on color additives used in the US
Color additives play a crucial role in capturing consumer attention and making food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and medical devices more appealing. However, the use of color additives in these products must adhere to strict regulations set forth by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure consumer safety.
In this article, GOL will provide you with an overview of FDA regulations on color additives to help you understand and comply with the law, ensuring the safety of your products for consumers.
1. What are color additives?
Color additives are substances added to foods, drugs, cosmetics, and other products to enhance or modify their color. These additives can be natural or synthetic, and they are used to improve the appearance of products, make them more appealing to consumers, or replace colors lost during processing or storage. In the food industry, color additives are regulated by government agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, which approves them for use only after they have been proven to be safe for consumption.

2. FDA Regulations on Color Additives
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) evaluates the safety of color additives and how the FDA ensures their compliance with these color additives in the United States, particularly the laws and regulations applicable to color additives.
History and Legal Framework
Regulations on color additives in the United States originated from the Federal Food and Drugs Act of 1906, also known as the Pure Food and Drug Act. This law prohibited the sale of adulterated food and drugs in the United States and banned the use of harmful or deleterious colors in confectionery and food products. The USDA was entrusted with verifying products that were adulterated or misbranded. In 1907, the USDA published the first list of safe coloring agents.
In 1927, regulatory oversight transferred to the Food, Drug, and Insecticide Administration, later becoming the FDA. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938 expanded the FDA’s regulatory scope to include cosmetics.
The FD&C regulations require the declaration of artificial colors on food labels and establish procedures for the approval and certification of new colors. Subsequent amendments raised safety standards and defined the safety evaluation factors of a color additive. The definition of “color additive” encompasses sources from plants, animals, minerals, and coal tar.
The use of color additives aims to enhance natural color and provide unique characteristics to products. They are often used at low concentrations and must comply with regulations regarding safe usage. The use of unsafe color additives is prohibited.
Importantly, there are no GRAS exemptions for color additives, meaning there are no exceptions for these substances if they are not safe.

Approval Process Before Purchasing Additional Color Additives
The FDA in Part 71 of 21 CFR describes the requirements and procedures for requesting the use of color additives. A supplemental color petition typically includes information on chemistry, toxicity, and the environment. Chemical information includes composition, manufacturing process, and physical and chemical properties. Toxicity information must demonstrate the safety of the color additive at the intended level of use. Environmental information assesses the impact of using the color additive on the environment.
Color additive petitions must be submitted to the FDA’s Office of Food Additive Safety (OFAS) for processing and review. The FDA will notify the requester of receipt within 15 days. If the petition is accepted, the FDA will publish a notice of filing in the Federal Register. If the petition is not accepted, the FDA will provide reasons, and the requester will have an opportunity to amend.
OFAS manages the petition review process. Scientists evaluate the chemical composition and uniformity of the color additive. They also review analytical methods to ensure compliance with specifications and assess safe usage levels. Toxicity evaluators review available information to ensure the safety of the color additive. Finally, environmental assessors review the environmental impact.
This process ensures that the use of color additives complies with safety and environmental standards.
3. What are color additives in food?
Color additives in food are substances added to food to enhance or alter the natural color of the food. The purposes of using food color additives include:
- Enhancing attractiveness: Color plays a crucial role in stimulating the palate and creating a sense of tastiness. Using color additives makes food visually appealing and attractive, capturing the attention of consumers.
- Compensating for color changes: During processing, storage, or transportation, the natural color of food may change or fade. Using color additives helps compensate for these changes, keeping the food visually appealing as originally intended.
- Marking flavor profiles: Some types of color additives are used to mark flavor profiles for food. For example, red color is often used in strawberry-flavored candies, while blue color is used in grape-flavored candies, and so on.
- Product differentiation: Using different colors can help differentiate various products of the same type. For instance, soft drinks may come in various colors such as orange, red, green, etc., to distinguish different flavors.
Food color additives can be categorized into two main types:
- Natural color additives: Extracted from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, minerals, or animals. Some examples of natural color additives include:
- Anthocyanin: Found in berries, grapes, purple cabbage, and eggplant.
- Beta-carotene: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and spinach.
- Chlorophyll: Found in spinach, spirulina algae, and other green vegetables.
- Artificial color additives: Synthesized in laboratories from chemical compounds. Some examples of artificial color additives include:
- Tartrazine (FD&C Yellow 5): commonly used in candies, soft drinks, and snack foods.
- Sunset Yellow FCF (FD&C Yellow 6): commonly used in ice cream, cereals, and sausages.
- Red 40: commonly used in candies, soft drinks, gelatin, and ice cream.
The use of food color additives has sparked much controversy. Some people are concerned that certain types of artificial color additives may cause health hazards, including allergies, hyperactivity, and attention deficit, even cancer. However, it is important to note that studies on the adverse effects of food color additives are still limited and have not reached a consensus.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for ensuring the safety of food color additives. All food color additives must be approved by the FDA before being used in food. The FDA relies on scientific evaluations to determine the safety of color additives.
Consumers can limit their exposure to food color additives by choosing minimally processed whole foods and reading food labels for ingredient information, including color additives. Some foods may note “no artificial color additives” on the label.
In summary, food color additives are substances added to food to enhance or alter its natural color. Color additives can be categorized into two main types: natural and artificial. The use of food color additives has sparked controversy, but consumers can limit their exposure by choosing minimally processed foods and reading food labels carefully.

4. What are color additives in cosmetics?
Color additives in cosmetics are substances added to impart color to the product. They can be found in various types of cosmetics, including lipstick, blush, eyeshadow, foundation, and more.
There are two main types of cosmetic color additives:
- Natural color additives: Extracted from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, minerals, or animals. Some examples of natural color additives include:
- Anthocyanin: Found in berries, grapes, purple cabbage, and eggplant.
- Beta-carotene: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and spinach.
- Chlorophyll: Found in spinach, spirulina algae, and other green vegetables.
- Artificial color additives: Synthesized in laboratories from chemical compounds. Some examples of artificial color additives include:
- FD&C Red 40: Commonly used in lipstick, blush, and eyeshadow.
- D&C Red 34: Commonly used in lipstick and blush.
- FD&C Yellow 5: Commonly used in eyeshadow and foundation.
The use of color additives in cosmetics has sparked controversy. Some people are concerned that certain types of artificial color additives may cause health hazards, including allergies, skin irritation, and even cancer. However, it is important to note that studies on the adverse effects of cosmetic color additives are still limited and have not reached a consensus.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for ensuring the safety of cosmetic color additives. However, the FDA does not directly regulate the use of color additives in cosmetics. Instead, the FDA relies on general regulations on cosmetic safety to ensure that products are safe for consumers.
Consumers can limit their exposure to cosmetic color additives by choosing products labeled “free of artificial color additives.” It is advisable to read cosmetic labels carefully to obtain information about ingredients, including color additives.
In summary, cosmetic color additives are substances added to impart color to the product. The use of cosmetic color additives has sparked controversy, but consumers can limit their exposure by choosing products labeled “free of artificial color additives.
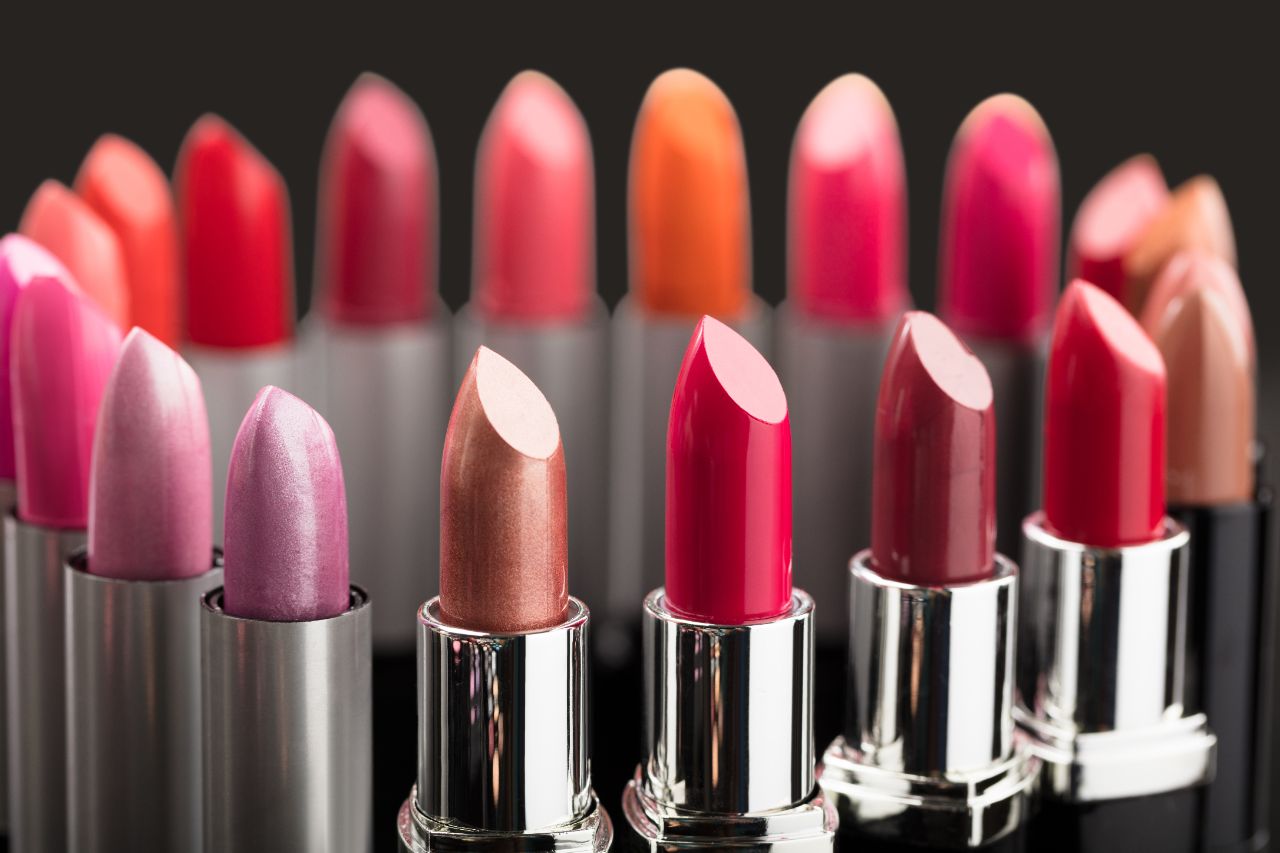

5. Color additives in drugs
Color additives in medicines are substances added to provide color to the medication. They can be derived from natural or synthetic sources. The primary purpose of color additives is to make medicines more visually appealing for patients to take. They may also be used to mask the bitter or unpleasant taste of the medication.
There are several different types of color additives that can be used in medicines. Some of the most common types include:
- FD&C colors: These are the most commonly used type of color additives in medicines. They are approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as safe for use in both food and drugs. Examples of FD&C colors include Red 40, Yellow 5, and Blue 1.
- Azo colors: This type of color additive is not as widely used as FD&C colors. However, they are still used in some types of medicines. Azo colors have been associated with some side effects, including allergies and hyperactivity. Examples of azo colors include tartrazine, sunset yellow, and red 28.
- Natural colors: These color additives are derived from plant, mineral, or animal sources. They are often considered safer than synthetic color additives. However, some people may still be allergic to natural colors. Examples of natural colors include beta-carotene, annatto, and caramel.
It is important to note that not everyone may tolerate color additives. Some individuals may be allergic to certain types of color additives, which can cause symptoms such as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any adverse reactions after taking medication, it is important to speak with your doctor.
Here are some additional information about color additives in medicines:
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of color additives in medicines. The FDA ensures that color additives are used safely and effectively.
- A list of color additives approved by the FDA for use in medicines is available on the FDA’s website.
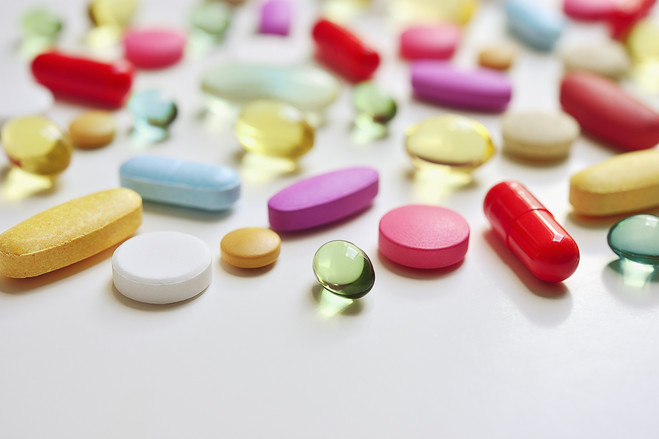

6. FAQs about fda color additives
Are color additives FDA approved?
Yes, with some exceptions. The FDA requires approval for most color additives before they can be used in food, drugs, cosmetics, or medical devices. There are two main categories:
- Certified color additives: These are typically synthetic and go through a stricter approval process to ensure safety. These are what people usually think of when they hear about color additives in food.
- Color additives exempt from certification: These are generally derived from natural sources like plants, minerals, or even insects (like carmine). Although they don’t require the same level of approval, they still need to be reviewed by the FDA for safety before being used.
Are color additives safe for consumption?
Indeed, color additives are deemed safe when utilized in compliance with FDA regulations. When the FDA grants approval for a color additive’s inclusion in food products, our regulations outline:
- The specific types of foods wherein it can be incorporated,
- Any prescribed maximum quantities permitted for usage, and
- Guidelines for how the color additive must be designated on the food packaging.
What is the most commonly used color additive?
There isn’t just one single most common color additive, but a trio that reign supreme: Red 40, Yellow 5, and Yellow 6. Estimates say these three account for roughly 90% of all dyes used in food
How can I determine if my food contains color additives?
Food manufacturers are mandated by the FDA to disclose all ingredients on the label, prioritizing those used in the largest quantities followed by those in smaller amounts. Any FDA-certified color additive, such as FD&C Blue No. 1 or its abbreviated form, Blue 1, must be explicitly listed. Except for carmine/cochineal extract, color additives exempt from certification can be grouped under general terms like “artificial colors,” “artificial color added,” “color added,” or similarly descriptive phrases, without individually naming each one. However, carmine/cochineal extract must be identified by name on food labels due to the potential for allergic reactions in some individuals.
The regulations regarding FDA color additives can be complex and difficult to navigate. However, understanding these rules is crucial to ensure compliance with the law and the safety of your products for consumers.
At GOL, we provide comprehensive FDA registration services to help you bring your products to market quickly and efficiently. Our experienced team of experts will guide you through each step of the registration process and ensure that your documentation is complete and compliant with all regulations. Contact us today to learn more about our FDA registration services for food, medical devices, and cosmetics.